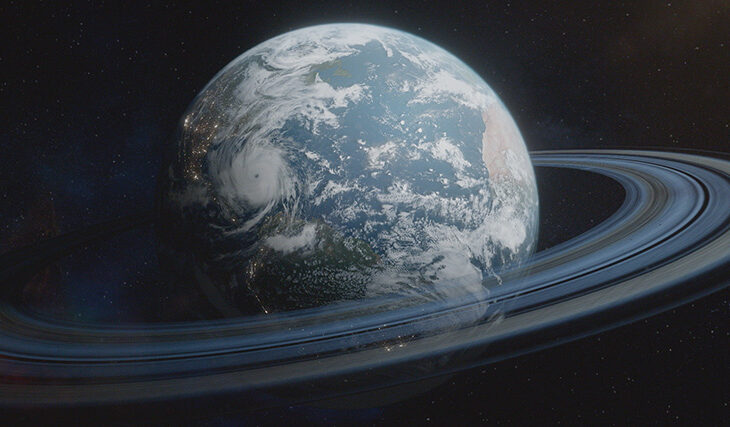
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune have rings.
When Theia crashed into the Earth, the Earth also had rings that formed into the Moon.
What is it like to live on a planet with rings?
How can rings appear on the Earth?
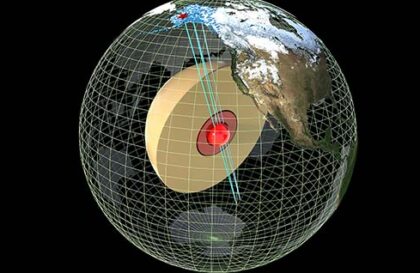
If the Moon is crushed again, it is enough to move it a little closer to the Earth, and the Earth will again have rings. The Moon must cross the limit of Rosh. This is the boundary where the larger body is torn apart by tidal forces. The Roche distance depends on the mass, density, and size of the bodies.
For example, the Sun is tearing up comets within 800,000 miles (1.3 million kilometers). The Earth is tearing apart an average comet at a distance of 11,000 miles (18,000 kilometers) from the surface.
For the Moon, the Roche limit is about 5,900 miles (9500 kilometers).
The rings from the moon will be made of stone. For example, Saturn has ice rings. They are 310 miles (500 km) wide and 9.5 meters thick (I was right, only 9.5 meters).
Earth with rings. How is that?
Earth’s rings enclosing the planet can have a significant impact on biological and atmospheric processes. Their presence can disrupt the navigational systems of some animals and affect plant photosynthesis and oxygen supply. The location of parts of the Earth in the shadow of the rings can lead to a deterioration in the conditions for life. The rings will also create an orbital obstacle to human spaceflight.
Changing the orientation of the ring during the day will lead to a change in the illumination of the earth’s surface and, accordingly, the impact on climate and weather. Reflected light from the Earth’s ring can affect the occurrence of solar and lunar eclipses. The presence of a ring around the Earth can also change the composition of the atmosphere due to prolonged changes in weather patterns.
The interaction of the ring and the Moon can change the tidal processes in the oceans.
The ring will look different at different latitudes. Near the equator it is a thin line on the horizon, near the Arctic Circle it is a hump, and in temperate latitudes, it will look like a giant arch.
The luminosity of the earth’s rings depends on their ability to reflect sunlight. Approximately 10% of the incident sunlight can be reflected by the rings, which is equivalent to the brightness of a 130-watt light bulb per square meter of surface.
One day, the rings will fall to Earth, as they do to Saturn.
Why can’t the Earth have rings?
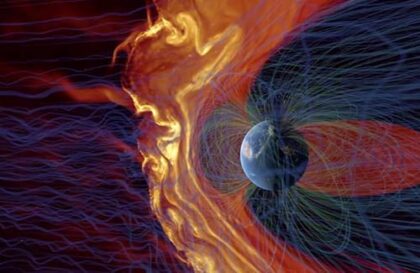
According to Linda Spilker, an expert on planetary ring systems at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the hypothetical configuration of the ring system around the Earth demonstrates instability, which could lead to its destruction in a relatively short, from an astronomical point of view, period. The main determinants of this instability are multiple factors, including the tidal influence from the Moon and the Sun, which has a destabilizing effect on the structure of the ring, as well as the influence of the solar wind, which sweeps out the smallest components of the ring structure located in near-Earth space.
Hypotheses about the existence of rings in the past
34 million years ago, the Earth could have had rings similar to those of Saturn. So says O’Keeffe of the Goddard Space Flight Center.
In 1980, O’Keeffe attributed the decrease in winter temperatures in the late Eocene to the fallout of a large number of tektites. The shading of the Earth by the ring could lead to global cooling, which is associated with the extinction of many species of marine organisms in the late Eocene.
According to scientists of the National Museum of Denmark for the period from 800 BC. e. to 1750 AD e. there were 16 such periods.
The Earth currently has two dust rings at an altitude of 600 km with an orbital inclination of 35.1 degrees. They consist of 6.4 particles per square kilometer per day. Particles from 1.8 mm in size.
Did the Earth still have rings?
On May 9, 1963, the US Air Force launched 480 million tiny copper needles, which briefly formed a ring around the entire globe. It was Project West Ford. They wanted to create an ionosphere for military communications. The package of needles weighed only 20 kg. The needles were placed in Earth orbit at an altitude between 350 and 380 kilometers. Each West Ford copper needle was 1.8 cm long, 0.0018 cm in diameter, and weighed only 40 micrograms.
They were designed to operate at exactly half the wavelength of the 8000 MHz microwave. Such a length would create strong reflections when the microwaves hit the copper needles.
The first connection attempt was successful. Using two 18.5-meter microwave dish antennas, Project West Ford engineers were able to transmit voice messages between Camp Parks, California, and Millstone Hill, Massachusetts. The voice connection was described as “intelligible” and was transmitted at approximately 20,000 bits per second—roughly the speed of a 1992-era telephone modem.
But a month later the project was closed. The needles began to spread, and the density of the ring decreased. On June 18, only 400 bits per second could be transmitted. Two months later, on July 2, the experiment was terminated.
This was not the only project to create artificial rings around the Earth.
The project of Nikola Tesla involved the construction of a solid ring around the Earth’s equator using a giant support system. After the construction is completed, the props must be removed, after which the ring should be suspended in space, rotating at the same speed as the Earth.
This idea was picked up by the American company Star Technology and Research. According to her project, the creation of a stone ring in equatorial orbit will reduce the flow of sunlight in the equatorial regions of the Earth and compensate for the impact of global warming. The cost of the project is estimated at 200 trillion US dollars.
Or perhaps somewhere in the Universe, there is a planet with rings, on which its inhabitants are discussing the question, what is it like to live without rings?
Image credit:
https://www.planetary.org
https://aboutislam.net