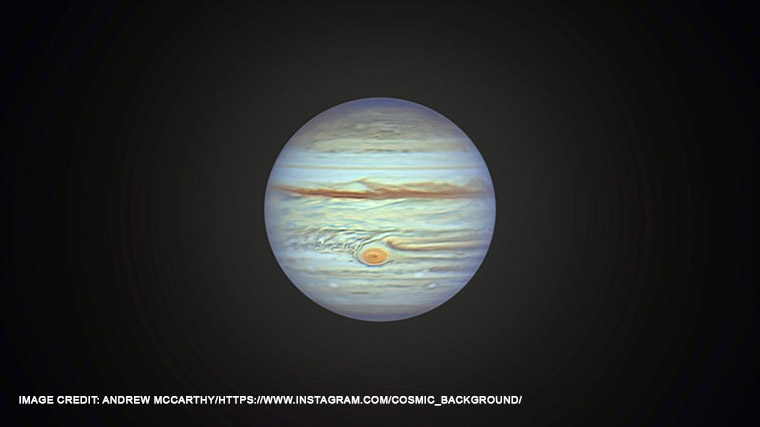
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest gas giant. The most famous phenomenon on Jupiter is the Great Red Spot. This powerful storm in the upper layers of the planet’s atmosphere has been raging for centuries and can be seen from Earth. Its size is impressive: at its maximum extent, the diameter of the Great Red Spot is approximately 16,350 kilometers (10,159 miles). This is several times the diameter of the Earth.
The Great Red Spot was discovered more than 300 years ago and remains one of the most massive and long-lived atmospheric structures on any planet in the Solar System. Italian astronomer Giovanni Domenico Cassini was the first to record observations of the Great Red Spot in 1665.
The nature and conservation of the great red spot
The Great Red Spot is known for its red or orange-pink color due to chemical reactions in the planet’s atmosphere. This color is usually associated with chemical compounds that contain phosphorus or sulfur.
Credit: ESA / Science & Exploration / Space Science / Juice
The Great Red Spot is located in a layer of the atmosphere dominated by clouds of ammonia and methane. The interaction of these chemical compounds with solar radiation can cause complex chemical reactions that affect the color and structure of the Great Red Spot.
There are also theories about the role of geostrophic currents and internal heat radiation in forming and maintaining the Great Red Spot. For some time, it was thought that this atmospheric feature might be a permanent phenomenon. Still, some observations show that its size decreases over time, possibly due to changes in the atmosphere’s chemical composition.
Observations of the Great Red Spot allow us to understand the atmospheric processes on Jupiter and the factors that influence the dynamics of the atmosphere of the gas giant.
Why does the Great Red Spot of Jupiter not affect the weather on Earth?
Despite its enormous size and obvious influence on Jupiter’s atmosphere, the Great Red Spot does not affect Earth’s weather.
And this has an explanation.
- Distance: The distance between Jupiter and Earth is too great for any direct influence. Jupiter is located at a distance of approximately 778 million kilometers from the Sun, which makes it impossible for it to have any significant influence on the atmosphere.
- Chemical composition: Jupiter’s atmosphere consists of clouds of ammonia and methane rather than nitrogen and oxygen, the main components of Earth’s atmosphere. Therefore, the chemical composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere cannot directly affect the Earth’s climate or weather.
- Timeline: The Great Red Spot is a stable atmospheric structure on Jupiter that has existed for centuries. The weather phenomena on Earth that we observe are on a much shorter time scale and depend on other factors such as solar radiation and ocean currents.
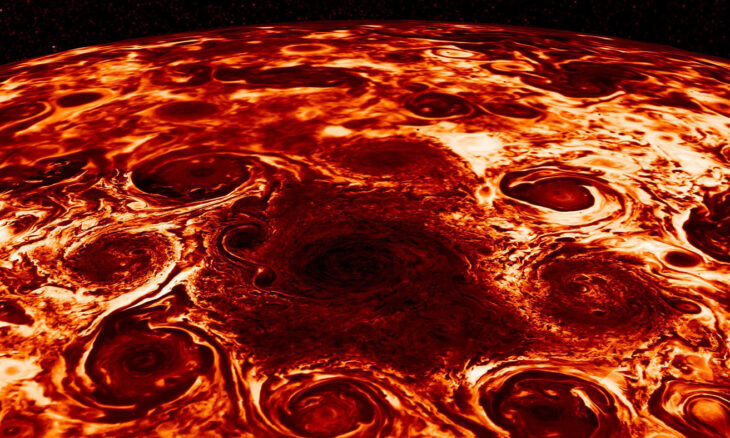
Other spots of Jupiter
The JunoCam imager aboard NASA’s Juno spacecraft captured this image of Jupiter’s southern equatorial region on Sept. 1, 2017. The image is oriented so Jupiter’s poles (not visible) run left-to-right of frame.
Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/MSSS/Kevin M. Gill
In addition to the Great Red Spot (GRES), there are other vortices on Jupiter, which, although more minor in size, remain quite impressive phenomena. These atmospheric spots can be of different colors, such as white, brown, and red, and last for decades or possibly much longer. Spots in Jupiter’s atmosphere were recorded in this planet’s southern and northern hemispheres. Interestingly, persistent spots that have existed for a long time are observed mainly in the southern hemisphere.
One exciting aspect of studying atmospheric spots on Jupiter is the possibility of collision of these vortices due to the difference in the speed of their movement in the planet’s atmosphere. Such collisions can lead, for example, to a change in the color of spots. One incident of such a collision occurred in 1975 when the color of the Great Red Spot changed several years after a crash with another atmospheric structure.
One example of these smaller atmospheric patches on Jupiter is Oval BA, which formed between 1998 and 2000 after the merger of three smaller white oval vortices observed for 60 years. Initially, this atmospheric structure was white in the visible range, but in February 2006, its color changed to reddish-brown. One of the hypotheses states that the spot’s color depends on the height at which it is located in the atmosphere. As long as the vortex is at the same height as the general surface of the upper edge of the atmosphere, it is white. However, as its power increases, the vortex rises higher, where, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation from the Sun, chemical reactions lead to a change in color, adding a red tint.
Giant atmospheric spots and vortices are observed on Jupiter and other gas planets of the Solar System. For example, the Great Dark Spot is known on Neptune and is also the object of research.
Banner image: NASA/JPL-Caltech/SwRI/ASI/INAF/JIR
Image credit:
https://solarsystem.nasa.gov
https://www.esa.int
https://www.jpl.nasa.gov