2022
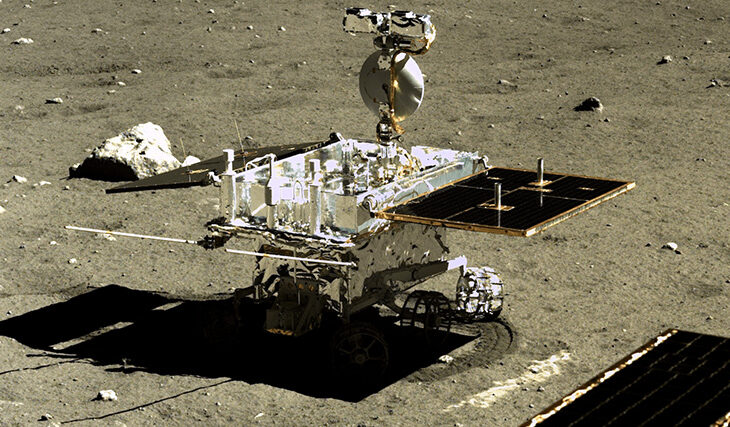
The Chinese lunar rover Yutu-2, exploring the far side of the moon, has discovered mysterious glass spheres. These spheres, larger than 1 inch (25 mm), can store important information about the composition of the Moon and its history of collisions. Previously, the lunar rover found the same spheres with a diameter of no more than 1 mm, created from silicate materials at high temperatures, as happens during volcanic eruptions and meteorite impacts.
According to scientists, the spheres found by Yutu-2 were probably formed as a result of meteorite impacts. Their translucent glassy luster indicates their volcanic origin, and later they may have been ejected by a meteorite impact, melted down, and re-formed into balls.
“Yutu-2” was intended for three months of work on the Moon. But he became the record holder for the longest stay on the Moon, providing information about the far side of the Moon, inaccessible from Earth. Thanks to him, we learned that the far side of the moon has stickier soil.
2023
Astronomers have been studying new Yutu-2 data taken from a depth of 300 meters below the lunar surface. There was nothing unusual in the first 40 meters – a crater covered with soil and dust. However, at depths ranging from 90 to 300 meters, hidden layers have been discovered, presumably indicative of multiple eruptions of basalt billions of years ago.
In total, five layers were identified, the thickness of which ranges from 20 to more than 70 meters. At least three of them contain volcanic rock basalt. This discovery allowed us to better understand what is hidden under the dusty surface of the moon.
In July 2023, astronomers also discovered a 3.5 billion-year-old solidified magma beneath the lunar surface, originating from a previously unknown type of volcano.
Image credit:
https://www.universetoday.com