What is the definition of low earth orbit (LEO)?
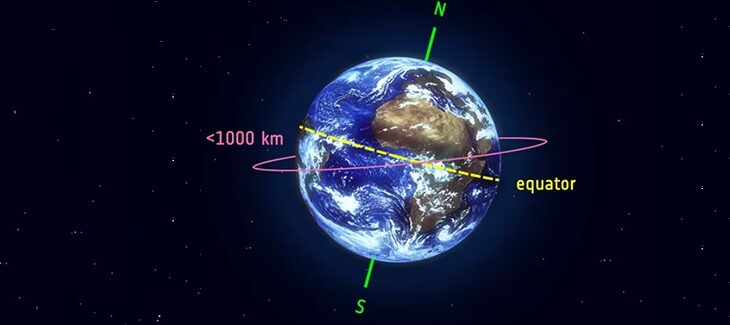
Low Earth Orbit (LEO) is a type of orbit around the Earth defined as having an altitude of less than 2,000 km (1,200 mi). It is commonly used to refer to space technology orbits ranging from about 160 km to about 2,000 km. LEO’s orbital period ranges from 88 minutes to about 127 minutes. The plane of the LEO orbit also maintains its orientation concerning the Sun as the Earth moves in its orbit, and at a given point on the Earth’s surface, the satellite always passes by at the same time of day.
LEO satellites also orbit at lower altitudes than geosynchronous satellites, and they orbit the Earth, making 12–16 Earth revolutions per Earth day. The International Space Station (ISS) uses low-altitude LEO orbits between 360 km and 440 km, with only 5 to 10 ms signal time delays. In addition, the satellites are visible for 5 to 20 minutes per orbit, depending on altitude, and users must be switched from satellite to satellite to maintain communication continuity.
Low Earth orbit is a type of orbit used for spacecraft. A polar orbit is a special type of low Earth orbit where the satellite is always above one point on the planet’s surface and is used to cover the entire planet. Various sensors in orbit can detect specular reflections from seas and oceans in low Earth orbit. NASA believes commercial projects can create an independent, sustainable, rapidly growing orbital economy. Finally, deploying more than one satellite in different orbital planes can improve availability because there are long periods when a satellite is out of sight of a particular ground station.
What are the advantages of low Earth orbit?
Credit: Cybera
Sun-synchronous orbits ensure consistent illumination of the Earth’s view and pass over the equator and every line of latitude at the same time each day. Satellites in LEO experience less atmospheric drag due to the lower density of the atmosphere, which also means that space tourism is possible in this orbit. LEO offers the advantage of deploying more satellites and CubeSats. In contrast, the solar array area for low-Earth orbit satellites must be as small as possible to reduce the fuel required to compensate for the drag effect. Satellites located in this orbit provide navigation, communication, and observation services.
Low Earth orbit is a crucial location for space research and experiments in astronomy and physics.
Banner image: ESA–L. Boldt-Christmas
Image credit:
https://www.esa.int
https://www.cybera.ca