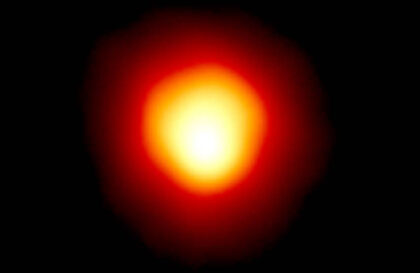
The star Arcturus, also known as Alpha Wolf (α Boötis), is one of the brightest stars in the night sky and the brightest star in the constellation Boötes. It is more than 110 times brighter than the Sun. This star has ancient historical significance and has played an important role in the navigation and cultural representations of various civilizations.
Arcturus is the fourth brightest star in the night sky after Sirius, Canopus and the Alpha Centauri system and the brightest star in the constellation Bootes. Its brightness is easily recognizable due to its orange or yellowish tint. The star is located in the northern sky, and its position can be determined by the well-known constellation Ursa Major.
The star belongs to the spectral type K0 III. It is an orange giant, which means that the star is in the stage of its evolutionary development, when it grew from an ordinary star like the Sun and began to expand and cool.
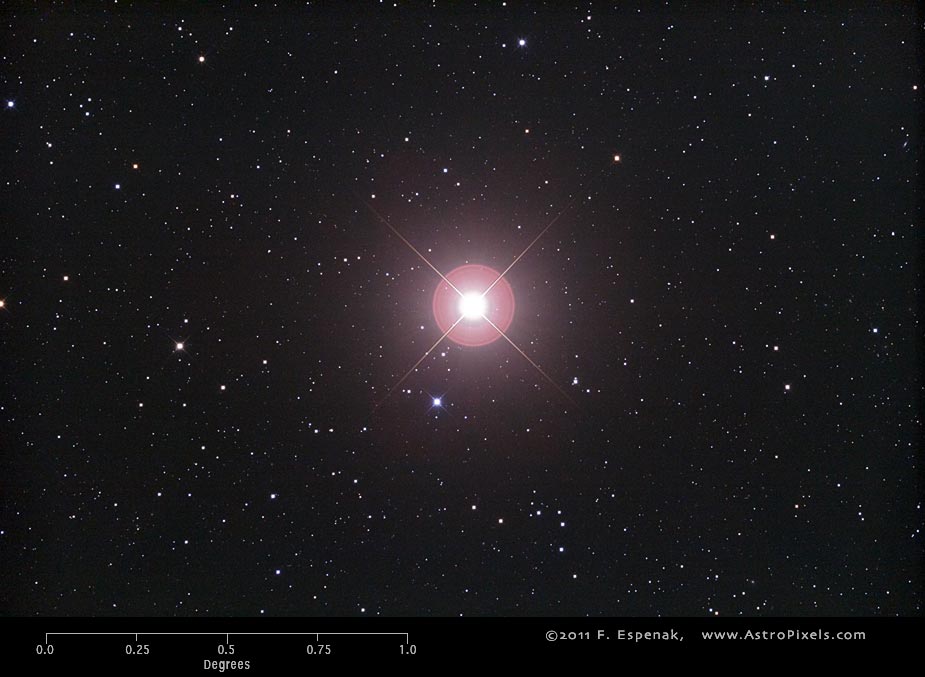
Estimates of the distance to Arcturus vary. According to the Hipparcos satellite, Arcturus is at a distance of 36.7 light years (11.3 parsecs) from Earth, which is quite close on a cosmic scale. This makes it one of the closest bright stars to us.
The high speed of Arcturus in outer space leads scientists to believe that this star was formed in another galaxy, which was subsequently absorbed by the Milky Way.
The name “Arcturus” comes from the ancient Greek word “Arktouros”, which means “guardian of the North”. Arcturus has had different names and meanings in different cultures, but in general it has been associated with navigation and the seasons.
Arcturus was also one of the first stars for which detailed observations were made. Solar spectra and comparisons with Arcturus have allowed astronomers to begin to decipher the characteristics and composition of stars. Arcturus was the first star other than the Sun to be seen during the day with a telescope. This was done in March 1635 by the French astronomer and astrologer Jean-Baptiste Morin
Constellation Bootes?
The constellation Boötes, also known as Boötes, is one of the brightest constellations in the night sky and home to the Boötes Void, a region of the universe 250 to 330 million light-years across that, according to NASA, is almost empty and contains only a few galaxies. . This is one of the most “empty” places in the universe. It has an ancient history and has played an important role in the mythology and navigation of different cultures.
The brightest star in the constellation Bootes and one of the brightest in the night sky is Arcturus (Alpha Wolf). This orange giant star is visible from Earth and is easily recognizable due to its bright orange color.
The constellation Bootes is an image of a man holding a club in one hand and a stick (or hair) in the other. This look has been associated with various legends and myths in different cultures. In Greek mythology, he is associated with Icarus, who tried to fly away with wings attached to the body of a wax cap. However, too close approach to the Sun broke the wax, and Icarus fell into the sea.
In some Asian cultures, the constellation Bootes has been associated with the legend of the Buddha. It is known as the “Walking Buddha” and this legend tells how the Buddha set out on his journey, leaving his footprints in the sky.
Bootes was used in navigation. It served as a landmark for navigators and peoples who relied on the stars to navigate the earth.
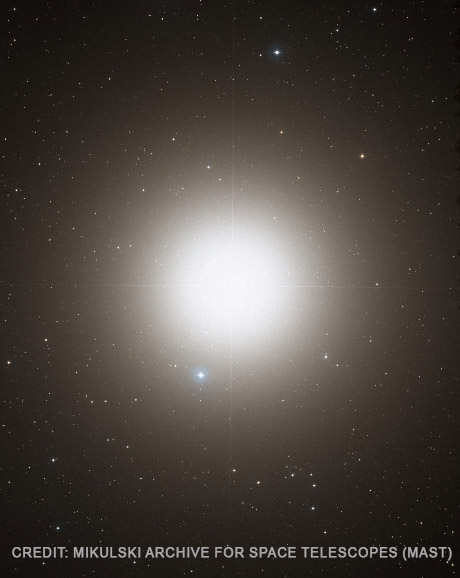

Celestial objects of the constellation Bootes?
Arcturus (α Boötis): The brightest star in the constellation and one of the brightest in the night sky. It is an orange giant star.
Izdijk (ι Boötis): A bright binary star composed of two components with different colors. She is often referred to as “Izdeyk” because of her English name “Mizar”.
Alcor (80 Ursae Majoris): A small star visible to the naked eye that was traditionally used to test for good eyesight. There is also a legend that allegedly in ancient Egypt, young men who could distinguish these stars were recruited into the elite troops of the pharaoh. This was proof that the vision was sharp enough. Versions of the legend feature Greek archers or Indian hunters. The “Arabic vision test” actually differs little from line 20/20 of the Snellen table (normal vision, acuity 1.0).
Messier 3 (M3): A globular cluster, one of the brightest and closest to Earth. It contains over 500,000 stars clustered into a dense ball.
Galaxy NGC 5248: A spiral galaxy seen through telescopes. It has beautiful spiral arms.
There are other, no less interesting objects.
Empty space in the universe?
The Boötes Void, also known as the “Butesian Void”, is a large region in the sky that is notorious for its lack of galaxies and stars. This is one of the most “empty” places in the Universe, where there are relatively few galaxies and stars.
It is located in the constellation Bootes (Butes) and is located approximately 230 million light-years from Earth.
Astronomers suggest that the Bootes Void was formed as a result of complex processes of gravitational interaction and the expansion of the Universe. Gravitational forces and interactions of galaxies could lead to the “cleansing” of matter from the area.
Interestingly it works. In some cases, gravity clears space, in other cases it condenses it. Wouldn’t it be nice to figure it out?
Image credit:
https://ru.wikipedia.org
https://spacegid.com/zvezda-arktur.html
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki